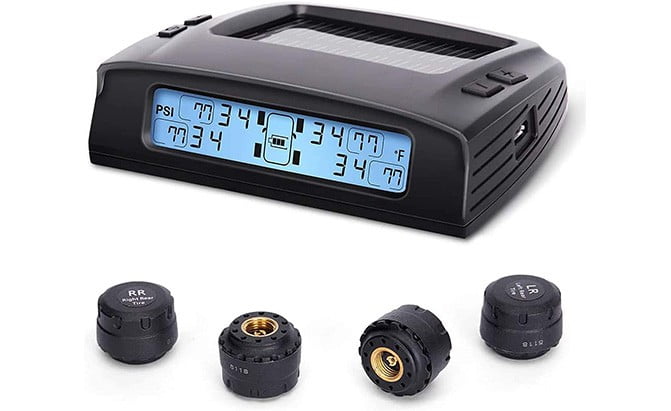
In today’s modern vehicles, tire safety is a top priority. Proper tire pressure is crucial for vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and road safety.
Vehicles are equipped with Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) to ensure that tires are always correctly inflated. TPMS technology can be categorized into two main types: direct and indirect TPMS.
This article will explore the differences between these two systems and understand their advantages and disadvantages.
What is a Tire Pressure Monitoring System?
Before diving into the differences between direct and indirect TPMS, it’s essential to understand the purpose and benefits of a TPMS in general.
Importance of Tire Pressure
Maintaining proper tire pressure is vital for various reasons:
- It ensures optimal vehicle handling and stability, enhancing overall safety on the road.
- Correctly inflated tires improve fuel efficiency, reducing the vehicle’s environmental impact.
- Maintaining the right tire pressure extends tire life and prevents premature wear and tear.
Benefits of a TPMS
A TPMS provides several advantages to vehicle owners. It constantly monitors tire pressure and alerts the driver when pressure levels are too low or too high.
This early warning system helps prevent tire-related accidents and increases driver confidence.
Additionally, a TPMS allows for proactive maintenance, enabling prompt action to rectify any tire pressure issues before they lead to more significant problems. So, check out official store.
Direct TPMS
Direct TPMS relies on sensors installed in each tire to monitor tire pressure individually. These sensors directly measure the pressure and temperature inside each tire and transmit the data to the vehicle’s onboard computer.
How Direct TPMS Works
Direct TPMS sensors are typically attached to the tire valve stem or incorporated into the tire pressure valve assembly. They use radio frequency to send tire pressure and temperature data wirelessly to the vehicle’s TPMS module. The module then processes this data and alerts the driver through a dashboard display or warning light if any tire’s pressure falls below the recommended level.
Advantages of Direct TPMS:
Direct TPMS offers several advantages over its indirect counterpart.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Direct TPMS provides real-time monitoring of individual tire pressures. This allows for precise and accurate readings, ensuring that deviations from the recommended pressure are immediately detected.
- Increased Accuracy: Direct TPMS sensors directly measure the tire pressure and provide highly accurate readings. This level of accuracy helps drivers maintain optimal tire pressure, improving safety and performance.
- Customizable Thresholds: Direct TPMS systems allow users to set customized pressure thresholds based on vehicle and tire specifications. This flexibility ensures drivers receive alerts when pressure levels deviate from their specific requirements.
- Temperature Compensation: Direct TPMS sensors also monitor tire temperature alongside pressure. Temperature fluctuations can impact tire pressure readings, and direct TPMS compensates for this factor, providing more reliable data.
- Enhanced Safety: With real-time monitoring and accurate readings, direct TPMS significantly enhances safety on the road. Drivers are promptly alerted to any significant changes in tire pressure, allowing them to take immediate action and prevent potential tire failures or accidents.
Disadvantages of Direct TPMS
While direct TPMS offers numerous benefits, it also has some drawbacks to consider:
- Cost: Direct TPMS systems tend to be more expensive than indirect systems. This is primarily due to the additional sensors required for each tire. However, the cost has been decreasing as the technology becomes more widespread.
- Maintenance: The individual sensors in direct TPMS systems require periodic maintenance. Battery replacement or sensor calibration may be necessary, adding to the overall maintenance costs.
- Installation Complexity: Installing direct TPMS sensors requires more effort and expertise. It involves mounting the sensors on the valve stems or integrating them into the tire pressure valve assembly. This complexity can increase installation time and costs.
- Tire Replacement Challenges: When replacing tires, the sensors in direct TPMS systems need to be removed from the old tires and reinstalled on the new ones. This process can be time-consuming and may require professional assistance.
Indirect TPMS
Indirect TPMS, as the name suggests, indirectly measures tire pressure by monitoring other vehicle parameters, such as wheel speed or ABS sensor data.
How Indirect TPMS Works
Indirect TPMS systems rely on the principle that underinflated tires have a slightly smaller diameter than properly inflated ones. By comparing the rotational speed of each tire, the system can estimate whether the pressure is within the recommended range.
Advantages of Indirect TPMS
While indirect TPMS has some limitations compared to direct TPMS, it does offer certain advantages:
- Lower Cost: Indirect TPMS systems are generally less expensive than their direct counterparts. Since they rely on existing vehicle sensors, there is no need for additional tire-mounted pressure sensors.
- Simplicity: Indirect TPMS systems are simpler in terms of installation and maintenance. They do not require individual sensors for each tire, reducing complexity and potential points of failure.
- Retrofitting: Indirect TPMS can be retrofitted to older vehicles that do not have a TPMS system. This allows owners of older vehicles to enjoy the benefits of tire pressure monitoring without significant modifications.
Comparison of Direct and Indirect TPMS
When comparing direct and indirect TPMS, several factors should be considered:
Accuracy
Direct TPMS provides more accurate and precise tire pressure readings than indirect TPMS. Direct TPMS can promptly detect and alert drivers to any significant deviations in tire pressure by directly measuring each tire’s pressure pressure pressure.
Cost
Direct TPMS generally has a higher upfront cost compared to indirect TPMS. The need for individual tire sensors and their installation can increase the overall system cost.
Additionally, the replacement cost for individual sensors can add to the expenses in case of sensor failure or damage. Indirect TPMS, on the other hand, utilizes the existing ABS, resulting in lower initial costs.
Maintenance
Direct TPMS requires periodic maintenance, including battery replacement for the sensors. While the battery life is typically long-lasting, eventually, they will need to be replaced. Indirect TPMS, on the other hand, has less maintenance involved since it doesn’t rely on individual sensors.
Tire Replacement
Regarding tire replacement, direct TPMS may require additional steps to transfer or reprogram sensors onto new tires. This process can incur additional costs and effort. Indirect TPMS doesn’t have this requirement since it doesn’t rely on individual tire sensors.
Considering these factors, it is important to weigh the accuracy, cost, maintenance, installation, and tire replacement requirements based on individual needs and preferences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) ensure tire safety, vehicle performance, and fuel efficiency. The two primary types of TPMS, direct and indirect, offer different approaches to tire pressure monitoring.
Direct TPMS provides accurate and real-time tire pressure information, allowing for individual tire monitoring. However, it comes with a higher upfront cost, sensor maintenance, and potential sensor replacement.
Indirect TPMS, on the other hand, relies on the ABS and offers a more cost-effective solution. While it may be less accurate and lacks individual tire pressure readings, it requires less maintenance and simplifies tire replacement.
Ultimately, the choice between direct and indirect TPMS depends on accuracy needs, budget, maintenance preferences, and installation considerations.