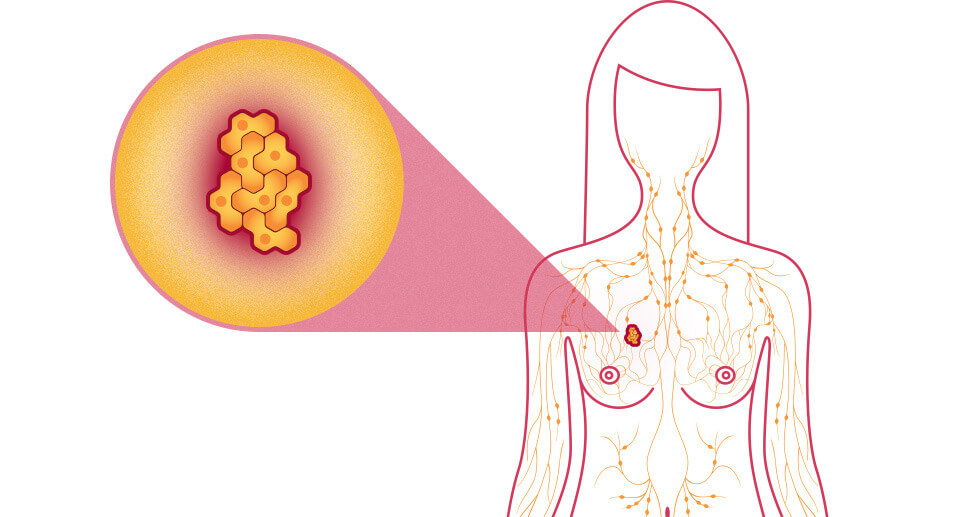
Throughout breast cancer, defective genes contribute to the unregulated growth of the breast cells and do not die as normal. When these cells are slowly growing and other tissues are not disturbed, they cause benign tumors.
Such bumps are typically not health-threatening. If irregular cell growth is quicker and tissue invasion occurs, cancerous tumors are created. Such tumors pose a danger and can spread to the whole body and cause new tumors.
But you don’t have to take tension because there are many breast lump removal treatments.
Fibroadenomas are benign and very normal (not cancer) growths. This increase is most common in women between the ages of 30 and 35, but can also be seen in women under the age of 30.
Fibroadenomas are strong, rigid, frequently painless, or tender tumors. Among adolescents or during pregnancy, they often grow rapidly.
In the United States, 1 woman in 8 resides in invasive breast cancer according to BreastCancer.org. In 2018, scientists estimated that more than 266,000 people in U.S. breast cancer will be diagnosed. In the USA, nearly 40.920 women are expected to die throughout 2018 of the condition.
Breast cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in American women. In 2017, it constituted about 30% of new cancer reports. Women are at a significantly lower rate, and the chance of survival is about 1 in 1,000 in the US.
1. Symptoms And Early Signs
In its early stages, breast cancer is often difficult to detect. Although others have lumps, pain, swelling, and skin changes during breast cancer, others may not experience obvious symptoms. Many forms of breast cancer have a new weight (or lump) in the American Cancer Society.
There May Also Be A Wide Range Of Other Signs, Including:
- Pain.
- Breast or nipple swelling, pain, or change in color.
- Retraction of the nipple.
- A new mole or an existing breast or mole modification.
- Nausea that will not heal on the breast or nipple.
- Tender or extended underarm or neck area glands.
[su_heading size=”15″ margin=”10″]You May Also Like – Why Regular Medical Check Ups Matter[/su_heading]
2. What Are The Breast Lump Forms And Causes? How Do They Look?

Breast lumps have many effects. Some of these causes are harmless and some can be painful. Breast lumps include diseases, fractures, cancer, and non-cancerous growth.
In the United States, breast cancer is the second largest cause of carcinogenic death in women. Today, breast cancer death rates are decreasing.
A combination of warmer identification, better screening, and improved care will lead to a decrease in death rates. Every breast lump should be examined by the doctor to exclude or determine a cancer diagnosis where most breast lumps were harmless (benign).
3. Infections
Mastitis is known for inflammation of the breast tissue. In women who breastfeed a baby (lactating), mastitis may occur. Bacteria may invade the damaged area and cause infections when the skin of a nipple (areola) is wounded or broken, which happens in nursing.
A hard area is commonly known as the’ clogged milk canal’ that can form in a lactating woman. Some treatments (see below) can prevent a painful, difficult area from becoming an actual breast infection.
Infections can either be a deep pus pocket in which the infection looks like a breast (an abscess) or a larger area of cellulite (cellulite) that spreads out.
4. Injuries To Breast
If a breast is traumatically injured, small blood vessels can burst to cause localized bleeding (hematoma) to appear as a lump.
The fat cells of the breast, a condition called fat necrosis, may suffer from trauma to the brain. A lump in the breast may form also the wound.
These lumps are not cancerous following a substantial trauma. At the site of previous breast biopsies, fat necrosis can also occur.